Table of Contents
- Kubernetes RBAC角色权限控制
[TOC]
Kubernetes RBAC角色权限控制
RBAC——基于角色的访问控制
Kubernetes RBAC角色权限控制
什么是 Kubernetes RBAC
在Kubernetes中,授权有ABAC(基于属性的访问控制)、RBAC(基于角色的访问控制)、Webhook、Node、AlwaysDeny(一直拒绝)和AlwaysAllow(一直允许)这6种模式。从1.6版本起,Kubernetes 默认启用RBAC访问控制策略(beta版本)。从1.8开始,RBAC已作为稳定的功能。通过设置–authorization-mode=RBAC,启用RABC。在RABC API中,通过如下的步骤进行授权:1)定义角色:在定义角色时会指定此角色对于资源的访问控制的规则;2)绑定角色:将主体与角色进行绑定,对用户进行访问授权。
基于角色的访问控制(Role-Based Access Control, 即 "RBAC"):使用 “rbac.authorization.k8s.io” API Group 实现授权决策,允许管理员通过 Kubernetes API 动态配置策略。
RBAC 从 Kubernetes v1.6 处于beta版本,从 v1.8 开始,RBAC已作为 稳定的功能。启用 RBAC,请使用 --authorization-mode=RBAC 启动 API Server。
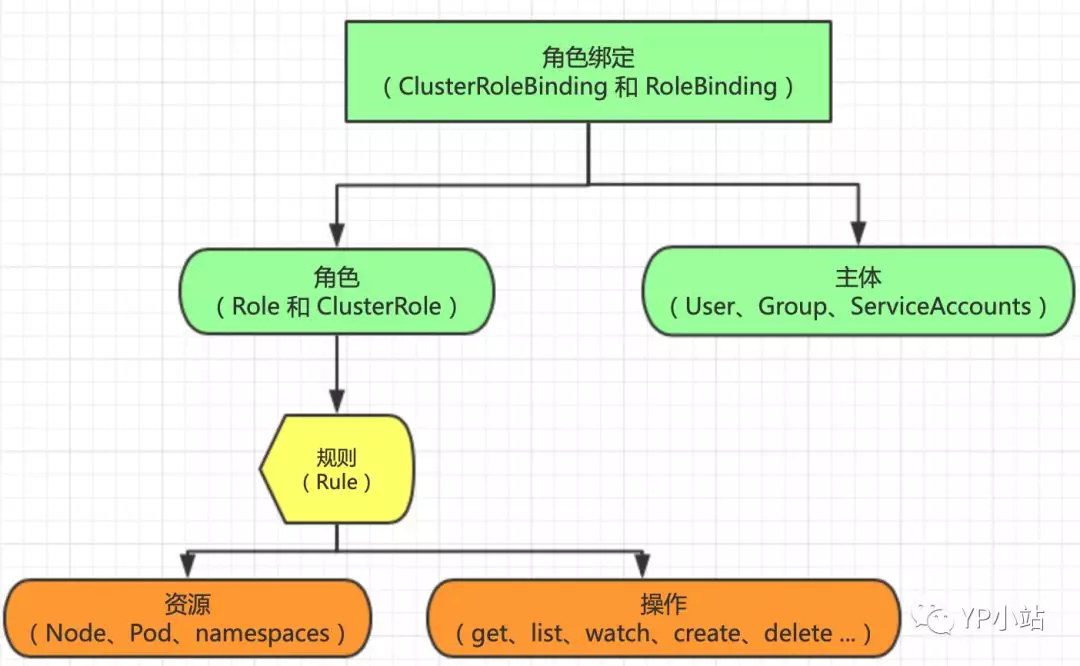
三个RBAC最基本的概念
- Role: 角色,它定义了一组规则,定义了一组对Kubernetes API对象的操作权限
- Subject: 被作用者,既可以是"人",也可以是机器,当然也可以是我们Kubernetes中定义的用户(ServiceAccount主要负责kubernetes内置用户)
- RoleBinding: 定义了"被作用者"和"角色"的绑定关系
在Kubernetes中所有的API对象都保存在ETCD里,可是,对这些API对象的操作,却一定是通过访问kube-apiserver实现的。我们需要APIServer来帮助我们授权工作,而在Kubernetes项目中,负责完成授权(Authorization)的工作机制就是RBAC: 基于角色的访问控制 (Role-Based Access Control)
RBAC是基于角色的访问控制 (Role-Based Access Control) 在RBAC中,权限与角色相关联。Kubernetes 基于角色的访问控制使用rbac.authorization.k8s.io API组来实现权限控制,RBAC允许管理员通过Kubernetes API动态的配置权限策略。如果需要开启RBAC授权需要在apiserver组件中指定--authorization-mode=Node,RBAC
ClusterRole 与 Role
在RBAC API中,角色包含代表权限集合的规则。在这里,权限只有被授予,而没有被拒绝的设置。在Kubernetes中有两类角色,即普通角色和集群角色。可以通过Role定义在一个命名空间中的角色,或者可以使用ClusterRole定义集群范围的角色。一个角色只能被用来授予访问单一命令空间中的资源。下面是在“default”命令空间中定义了一个名为“pod-reader”的角色,此角色能够对在“default”命名空间中访问Pod.
Role(角色)
是一系列权限的集合,例如一个角色可以包含读取 Pod 的权限和列出 Pod 的权限。Role 只能用来给某个特定 namespace 中的资源作鉴权。对 namespace 、集群级资源 和 非资源类的 API(如 /healthz)使用 ClusterRole
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # 空字符串""表明使用 core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
上面的例子描述了 ”default” 命名空间中的一个 Role 对象的定义,用于授予对 pod 的读访问权限。
ClusterRole
对象可以授予与 Role 对象相同的权限,但由于它们属于集群范围对象,也可以使用它们授予对以下几种资源的访问权限:
- 集群范围资源(例如节点,即 node)
- 非资源类型 endpoint(例如 /healthz)
- 跨所有命名空间的命名空间范围资源(例如 pod,需要运行命令 kubectl get pods --all-namespaces 来查询集群中所有的 pod)
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
# ClusterRole 是集群范围对象,所以不需要定义 "namespace" 字段
name: secret-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"] #明确资源类型
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
上面例子中的 ClusterRole 定义可用于授予用户对某一特定命名空间,或者所有命名空间中的 secret(取决于其绑定方式)的读访问权限
Kubernetes还提供了四个预先定义好的ClusterRole来提供用户直接使用
- cluster-admin
- admin
- edit
- view
其中cluster-admin角色,对应的是整个Kubernetes项目中最高权限(verbs=*)
我们可以通过下面的命令查看clusterrole的权限
[root@node1 ~]# kubectl describe clusterrole cluster-admin -n kube-system
Name: cluster-admin
Labels: kubernetes.io/bootstrapping=rbac-defaults
Annotations: rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: true
PolicyRule:
Resources Non-Resource URLs Resource Names Verbs
--------- ----------------- -------------- -----
*.* [] [] [*]
[*] [] [*]
ClusterRoleBinding 与 RoleBinding
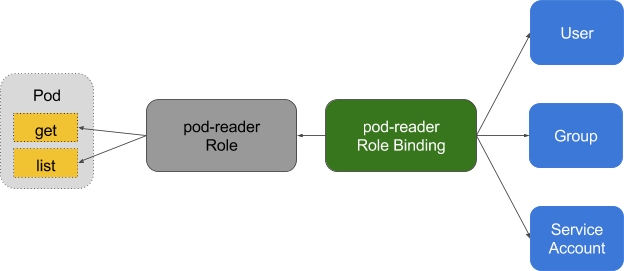
RoleBinding:
把 Role 或 ClusterRole 中定义的各种权限映射到 User,Service Account 或者 Group,从而让这些用户继承角色在 namespace 中的权限。
RoleBinding 可以引用在同一命名空间内定义的 Role 对象。
# 以下角色绑定定义将允许用户 "jane" 从 "default" 命名空间中读取 pod。
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: read-pods
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: User
name: jane
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: pod-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
RoleBinding 对象也可以引用一个 ClusterRole 对象用于在 RoleBinding 所在的命名空间内授予用户对所引用的 ClusterRole 中定义的命名空间资源的访问权限。
这一点允许管理员在整个集群范围内首先定义一组通用的角色,然后再在不同的命名空间中复用这些角色。
例如,尽管下面示例中的 RoleBinding 引用的是一个 ClusterRole 对象,但是用户 ”dave” (即角色绑定主体)还是只能读取 ”development” 命名空间中的
secret(即 RoleBinding 所在的命名空间)。
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: read-secrets
namespace: development # 这里表明仅授权读取 "development" 命名空间中的资源。
subjects:
- kind: User
name: dave
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: secret-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
ClusterRoleBinding:
让用户继承 ClusterRole 在整个集群中的权限。
使用 ClusterRoleBinding 在集群级别和所有命名空间中授予权限。下面示例中所定义的 ClusterRoleBinding 允许在用户组 ”manager” 中的任何用户都可以读取
集群中任何命名空间中的 secret。
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: read-secrets-global
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: manager
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: secret-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
ClusterRole 聚合
从 v1.9 开始,在 ClusterRole 中可以通过 aggregationRule 来与其他 ClusterRole 聚合使用:
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: monitoring
aggregationRule:
clusterRoleSelectors:
- matchLabels:
rbac.example.com/aggregate-to-monitoring: "true"
rules: [] # Rules are automatically filled in by the controller manager.
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: monitoring-endpoints
labels:
rbac.example.com/aggregate-to-monitoring: "true"
# These rules will be added to the "monitoring" role.
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services", "endpoints", "pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
ServiceAccount
ServiceAccount主要负责kubernetes内置用户,下面简单定义一个ServiceAccount
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
namespace: mynamespace
name: example-sa
我们定义了一个serverAccount对象,只需要name以及namespace最基础字段就可以。然后通过编写rolebinding的yaml文件,来为这个serviceAccount分配权限
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: example-rolebinding
namespace: mynamespace
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: example-sa
namespace: mynamespace
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: example-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
在Rolebinding对象里,subject字段的类型(kind),不在是一个User,而是一个名叫example-sa的ServerAccount。而roleRef引用的Role对象,依然名叫example-role。也就是我们上面定义的
User && Group
Kubernetes除了有用户(User),还拥有用户组(Group)概念,如果我们Kubernetes配置了外部认证服务的话,这个用户组的概念就由外部认证服务提供
一个ServiceAccount在Kubernetes对应的用户的名字是
system:serviceaccount:<ServiceAccount名字>
而对应的用户组则是
system:serviceaccounts:<Namespace名字>
比如,我们可以在RoleBinding中定义如下subjects
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts:mynamespace
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
这就意味着role的规则权限,作用于mynamespace里的所有ServiceAccount,这就用到了用户组的概念
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
这个role的规则权限,则作用于整个系统里ServiceAccount
在Kubernetes中已经内置了很多歌为系统保留的ClusterRole,它们的名字都以system:开头,可以使用kubectl get clusterroles查找到
[root@node1 ~]# kubectl get clusterroles
NAME AGE
admin 3d21h
cluster-admin 3d21h
custom-metrics-resource-reader 3h22m
custom-metrics-server-resources 3h22m
edit 3d21h
flannel 3d21h
prometheus 3h23m
system:aggregate-to-admin 3d21h
system:aggregate-to-edit 3d21h
system:aggregate-to-view 3d21h
system:auth-delegator 3d21h
system:basic-user 3d21h
system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:nodeclient 3d21h
system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:selfnodeclient 3d21h
system:controller:attachdetach-controller 3d21h
system:controller:certificate-controller 3d21h
system:controller:clusterrole-aggregation-controller 3d21h
system:controller:cronjob-controller 3d21h
system:controller:daemon-set-controller 3d21h
system:controller:deployment-controller 3d21h
system:controller:disruption-controller 3d21h
system:controller:endpoint-controller 3d21h
system:controller:expand-controller 3d21h
system:controller:generic-garbage-collector 3d21h
system:controller:horizontal-pod-autoscaler 3d21h
system:controller:job-controller 3d21h
system:controller:namespace-controller 3d21h
system:controller:node-controller 3d21h
system:controller:persistent-volume-binder 3d21h
system:controller:pod-garbage-collector 3d21h
system:controller:pv-protection-controller 3d21h
system:controller:pvc-protection-controller 3d21h
system:controller:replicaset-controller 3d21h
system:controller:replication-controller 3d21h
system:controller:resourcequota-controller 3d21h
system:controller:route-controller 3d21h
system:controller:service-account-controller 3d21h
system:controller:service-controller 3d21h
system:controller:statefulset-controller 3d21h
system:controller:ttl-controller 3d21h
system:coredns 3d21h
system:csi-external-attacher 3d21h
system:csi-external-provisioner 3d21h
system:discovery 3d21h
system:heapster 3d21h
system:kube-aggregator 3d21h
system:kube-controller-manager 3d21h
system:kube-dns 3d21h
system:kube-scheduler 3d21h
system:kubelet-api-admin 3d21h
system:metrics-server 3h25m
system:node 3d21h
system:node-bootstrapper 3d21h
system:node-problem-detector 3d21h
system:node-proxier 3d21h
system:persistent-volume-provisioner 3d21h
system:public-info-viewer 3d21h
system:volume-scheduler 3d21h
view 3d21h
现在我们可以理解,所谓的角色(Role),其实就是一组规则权限列表,而我们分配这些权限的方式,就是通过创建RoleBinding对象,将被用者(subject)和权限列表绑定。
而对应的ClusterRole和ClusterRoleBinding,则是Kubernetes集群级别的Role和RoleBinding,它们不受namespace限制
对资源的引用
RBAC API对象
Kubernetes有一个很基本的特性就是它的所有资源都是模型化的API对象,允许执行CRUD(Create、Read、Update、Delete)操作。资源如下
主要的资源包括:
- Pods
- Nodes
- Services
- Deployment
- Replicasets
- Statefulsets
- Namespace
- Persistents
- Secrets
- ConfigMaps
- ...
资源对象可能存在的操作有如下:
- create
- get
- delete
- list
- update
- edit
- watch
- exec
这些资源和API Group进行关联,比如Pods属于Core API Group,而Deployment属于apps API Group,要在kubernetes中进行RBAC授权
大多数资源由代表其名字的字符串表示,例如 ”pods”,就像它们出现在相关API endpoint 的URL中一样。然而,有一些Kubernetes API还 包含了”子资源”,比如 pod 的 logs。在Kubernetes中,pod logs endpoint的URL格式为:
GET /api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/pods/{name}/log
在这种情况下,”pods” 是命名空间资源,而 ”log” 是 pods 的子资源。为了在 RBAC Role 中表示出这一点,我们需要使用斜线来划分资源与子资源。
如果需要 Role 绑定主体读取 pods 以及 pods log(如果不显示指定子资源,那么子资源是没有权限访问的),需要定义以下 Role
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-and-pod-logs-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods", "pods/log"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
上面的例子显示,“pod-and-pod-logs-reader”角色能够对“pods”和“pods/log”进行访问
通过 resourceNames 列表,Role可以针对不同种类的请求根据资源名引用资源实例。当指定了 resourceNames 列表时,不同动作种类的请求的权限,
如使用 ”get”、”delete”、”update” 以及 ”patch” 等动词的请求,将被限定到资源列表中所包含的资源实例上。
例如,如果需要限定一个角色绑定主体只能 ”get” 或者 ”update” 一个名为 “my-configmap” 的 configmap 时,可以定义以下角色:
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: configmap-updater
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmap"]
resourceNames: ["my-configmap"]
verbs: ["update", "get"]
值得注意的是,如果设置了resourceNames,则请求所使用的动词不能是list、watch、create或者deletecollection。 由于资源名不会出现在create、list、watch和deletecollection等API请求的URL中,所以这些请求动词不会被设置了resourceNames 的规则所允许,因为规则中的resourceNames部分不会匹配这些请求。
角色定义的例子
使用 kubectl api-resources 查看所有 kubernetes 资源对象所属的 apiGroups
[root@node1 ~]# kubectl api-resources
NAME SHORTNAMES APIGROUP NAMESPACED KIND
bindings true Binding
componentstatuses cs false ComponentStatus
configmaps cm true ConfigMap
endpoints ep true Endpoints
events ev true Event
limitranges limits true LimitRange
namespaces ns false Namespace
nodes no false Node
persistentvolumeclaims pvc true PersistentVolumeClaim
persistentvolumes pv false PersistentVolume
pods po true Pod
podtemplates true PodTemplate
replicationcontrollers rc true ReplicationController
resourcequotas quota true ResourceQuota
secrets true Secret
serviceaccounts sa true ServiceAccount
services svc true Service
mutatingwebhookconfigurations admissionregistration.k8s.io false MutatingWebhookConfiguration
validatingwebhookconfigurations admissionregistration.k8s.io false ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
customresourcedefinitions crd,crds apiextensions.k8s.io false CustomResourceDefinition
apiservices apiregistration.k8s.io false APIService
controllerrevisions apps true ControllerRevision
daemonsets ds apps true DaemonSet
deployments deploy apps true Deployment
replicasets rs apps true ReplicaSet
statefulsets sts apps true StatefulSet
tokenreviews authentication.k8s.io false TokenReview
localsubjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io true LocalSubjectAccessReview
selfsubjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io false SelfSubjectAccessReview
selfsubjectrulesreviews authorization.k8s.io false SelfSubjectRulesReview
subjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io false SubjectAccessReview
horizontalpodautoscalers hpa autoscaling true HorizontalPodAutoscaler
cronjobs cj batch true CronJob
jobs batch true Job
certificatesigningrequests csr certificates.k8s.io false CertificateSigningRequest
leases coordination.k8s.io true Lease
events ev events.k8s.io true Event
ingresses ing extensions true Ingress
nodes metrics.k8s.io false NodeMetrics
pods metrics.k8s.io true PodMetrics
ingresses ing networking.k8s.io true Ingress
networkpolicies netpol networking.k8s.io true NetworkPolicy
runtimeclasses node.k8s.io false RuntimeClass
poddisruptionbudgets pdb policy true PodDisruptionBudget
podsecuritypolicies psp policy false PodSecurityPolicy
clusterrolebindings rbac.authorization.k8s.io false ClusterRoleBinding
clusterroles rbac.authorization.k8s.io false ClusterRole
rolebindings rbac.authorization.k8s.io true RoleBinding
roles rbac.authorization.k8s.io true Role
priorityclasses pc scheduling.k8s.io false PriorityClass
csidrivers storage.k8s.io false CSIDriver
csinodes storage.k8s.io false CSINode
storageclasses sc storage.k8s.io false StorageClass
volumeattachments storage.k8s.io false VolumeAttachment
如果 apiGroups: [""] 则表示 core API Group。
在以下示例中,我们仅截取展示了rules部分的定义。
允许读取 core API Group 中定义的资源 ”pods”:
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
允许读写在 ”extensions” 和 ”apps” API Group 中定义的 ”deployments”:
rules:
- apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
允许读取”pods”以及读写”jobs”:
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["batch", "extensions"]
resources: ["jobs"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
允许读取一个名为”my-config”的ConfigMap实例(需要将其通过RoleBinding绑定从而限制针对某一个命名空间中定义的一个ConfigMap实例的访问):
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
resourceNames: ["my-config"]
verbs: ["get"]
允许读取core API Group中的”nodes”资源(由于Node是集群级别资源,所以此ClusterRole定义需要与一个ClusterRoleBinding绑定才能有效):
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
允许对非资源endpoint “/healthz”及其所有子路径的”GET”和”POST”请求(此ClusterRole定义需要与一个ClusterRoleBinding绑定才能有效):
rules:
- nonResourceURLs: ["/healthz", "/healthz/*"] # 在非资源URL中,'*'代表后缀通配符
verbs: ["get", "post"]
绑定用户能查看所有 namespace
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
# 鉴于ClusterRole是集群范围对象,所以这里不需要定 义"namespace"字段
name: view-namespace-clusterrole
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- namespaces
- namespaces/status
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
定义 develop-role 用户对 default 命名空间详细权限
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: develop-role
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- endpoints
- serviceaccounts
- configmaps
- persistentvolumeclaims
- persistentvolumes
- services
- replicationcontrollers
- replicationcontrollers/scale
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- pods/log
- pods/status
- pods/exec
verbs:
- create
- delete
- deletecollection
- patch
- update
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- bindings
- events
- limitranges
- namespaces/status
- replicationcontrollers/status
- resourcequotas
- resourcequotas/status
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- daemonsets
- statefulsets
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
- deployments/scale
- replicasets
- replicasets/scale
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- update
- apiGroups:
- autoscaling
resources:
- horizontalpodautoscalers
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- batch
resources:
- cronjobs
- jobs
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- extensions
resources:
- daemonsets
- statefulsets
- ingresses
- networkpolicies
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- extensions
resources:
- deployments
- deployments/scale
- replicasets
- replicasets/scale
- replicationcontrollers/scale
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- update
- apiGroups:
- policy
resources:
- poddisruptionbudgets
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- networkpolicies
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
对角色绑定主体(Subject)的引用
RoleBinding或者ClusterRoleBinding将角色绑定到角色绑定主体(Subject)。 角色绑定主体可以是用户组(Group)、用户(User)或者服务账户(Service Accounts)。
用户由字符串表示。可以是纯粹的用户名,例如”alice”、电子邮件风格的名字,如 “bob@example.com” 或者是用字符串表示的数字id。由Kubernetes管理员配置认证模块 以产生所需格式的用户名。对于用户名,RBAC授权系统不要求任何特定的格式。然而,前缀system:是 为Kubernetes系统使用而保留的,所以管理员应该确保用户名不会意外地包含这个前缀。
Kubernetes中的用户组信息由授权模块提供。用户组与用户一样由字符串表示。Kubernetes对用户组 字符串没有格式要求,但前缀system:同样是被系统保留的。
服务账户拥有包含 system:serviceaccount:前缀的用户名,并属于拥有system:serviceaccounts:前缀的用户组。
角色绑定的一些例子
以下示例中,仅截取展示了RoleBinding的subjects字段。
一个名为”alice@example.com”的用户:
subjects:
- kind: User
name: "alice@example.com"
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
一个名为”frontend-admins”的用户组:
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: "frontend-admins"
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kube-system命名空间中的默认服务账户:
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: kube-system
名为”qa”命名空间中的所有服务账户:
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts:qa
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
在集群中的所有服务账户:
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
所有认证过的用户(version 1.5+):
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:authenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
所有未认证的用户(version 1.5+):
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:unauthenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
所有用户(version 1.5+):
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:authenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- kind: Group
name: system:unauthenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
默认角色与默认角色绑定
API Server会创建一组默认的ClusterRole和ClusterRoleBinding对象。 这些默认对象中有许多包含system:前缀,表明这些资源由Kubernetes基础组件”拥有”。 对这些资源的修改可能导致非功能性集群(non-functional cluster)。一个例子是system:node ClusterRole对象。 这个角色定义了kubelets的权限。如果这个角色被修改,可能会导致kubelets无法正常工作。
所有默认的ClusterRole和ClusterRoleBinding对象都会被标记为kubernetes.io/bootstrapping=rbac-defaults。
自动更新
每次启动时,API Server都会更新默认ClusterRole所缺乏的各种权限,并更新默认ClusterRoleBinding所缺乏的各个角色绑定主体。 这种自动更新机制允许集群修复一些意外的修改。由于权限和角色绑定主体在新的Kubernetes释出版本中可能变化,这也能够保证角色和角色 绑定始终保持是最新的。
如果需要禁用自动更新,请将默认ClusterRole以及ClusterRoleBinding的rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate 设置成为false。 请注意,缺乏默认权限和角色绑定主体可能会导致非功能性集群问题。
自Kubernetes 1.6+起,当集群RBAC授权器(RBAC Authorizer)处于开启状态时,可以启用自动更新功能.
发现类角色
| 默认ClusterRole | 默认ClusterRoleBinding | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| system:basic-user | system:authenticated and system:unauthenticated groups | 允许用户只读访问有关自己的基本信息。 |
| system:discovery | system:authenticated and system:unauthenticated groups | 允许只读访问API discovery endpoints, 用于在API级别进行发现和协商。 |
面向用户的角色
一些默认角色并不包含system:前缀,它们是面向用户的角色。 这些角色包含超级用户角色(cluster-admin),即旨在利用ClusterRoleBinding(cluster-status)在集群范围内授权的角色, 以及那些使用RoleBinding(admin、edit和view)在特定命名空间中授权的角色。
| 默认ClusterRole | 默认ClusterRoleBinding | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| cluster-admin | system:masters group | 超级用户权限,允许对任何资源执行任何操作。 在ClusterRoleBinding中使用时,可以完全控制集群和所有命名空间中的所有资源。 在RoleBinding中使用时,可以完全控制RoleBinding所在命名空间中的所有资源,包括命名空间自己。 |
| admin | None | 管理员权限,利用RoleBinding在某一命名空间内部授予。 在RoleBinding中使用时,允许针对命名空间内大部分资源的读写访问, 包括在命名空间内创建角色与角色绑定的能力。 但不允许对资源配额(resource quota)或者命名空间本身的写访问。 |
| edit | None | 允许对某一个命名空间内大部分对象的读写访问,但不允许查看或者修改角色或者角色绑定。 |
| view | None | 允许对某一个命名空间内大部分对象的只读访问。 不允许查看角色或者角色绑定。 由于可扩散性等原因,不允许查看secret资源。 |
Core Component Roles(核心组件角色)
| 默认ClusterRole | 默认ClusterRoleBinding | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| system:kube-scheduler | system:kube-scheduler user | 允许访问kube-scheduler组件所需要的资源。 |
| system:kube-controller-manager | system:kube-controller-manager user | 允许访问kube-controller-manager组件所需要的资源。 单个控制循环所需要的权限请参阅控制器(controller)角色. |
| system:node | system:nodes group (deprecated in 1.7) | 允许对kubelet组件所需要的资源的访问,包括读取所有secret和对所有pod的写访问。 自Kubernetes 1.7开始, 相比较于这个角色,更推荐使用Node authorizer 以及NodeRestriction admission plugin, 并允许根据调度运行在节点上的pod授予kubelets API访问的权限。 自Kubernetes 1.7开始,当启用Node授权模式时,对system:nodes用户组的绑定将不会被自动创建。 |
| system:node-proxier | system:kube-proxy user | 允许对kube-proxy组件所需要资源的访问。 |
其它组件角色
| 默认ClusterRole | 默认ClusterRoleBinding | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| system:auth-delegator | None | 允许委托认证和授权检查。 通常由附加API Server用于统一认证和授权。 |
| system:heapster | None | Heapster组件的角色。 |
| system:kube-aggregator | None | kube-aggregator组件的角色。 |
| system:kube-dns | kube-dns service account in the kube-systemnamespace | kube-dns组件的角色。 |
| system:node-bootstrapper | None | 允许对执行Kubelet TLS引导(Kubelet TLS bootstrapping)所需要资源的访问. |
| system:node-problem-detector | None | node-problem-detector组件的角色。 |
| system:persistent-volume-provisioner | None | 允许对大部分动态存储卷创建组件(dynamic volume provisioner)所需要资源的访问。 |
控制器(Controller)角色
Kubernetes controller manager负责运行核心控制循环。 当使用--use-service-account-credentials选项运行controller manager时,每个控制循环都将使用单独的服务账户启动。 而每个控制循环都存在对应的角色,前缀名为system:controller:。 如果不使用--use-service-account-credentials选项时,controller manager将会使用自己的凭证运行所有控制循环,而这些凭证必须被授予相关的角色。 这些角色包括:
system:controller:attachdetach-controller
system:controller:certificate-controller
system:controller:cronjob-controller
system:controller:daemon-set-controller
system:controller:deployment-controller
system:controller:disruption-controller
system:controller:endpoint-controller
system:controller:generic-garbage-collector
system:controller:horizontal-pod-autoscaler
system:controller:job-controller
system:controller:namespace-controller
system:controller:node-controller
system:controller:persistent-volume-binder
system:controller:pod-garbage-collector
system:controller:replicaset-controller
system:controller:replication-controller
system:controller:resourcequota-controller
system:controller:route-controller
system:controller:service-account-controller
system:controller:service-controller
system:controller:statefulset-controller
system:controller:ttl-controller
Permissive RBAC(宽泛的RBAC权限)
所谓 Permissive RBAC 是指授权给所有的 Service Accounts 管理员权限。
您可以使用RBAC角色绑定来复制一个宽泛的策略。
警告:以下政策略允许所有服务帐户作为集群管理员。 运行在容器中的任何应用程序都会自动接收服务帐户凭据,并且可以对API执行任何操作,包括查看secret和修改权限。 因此,并不推荐使用这种策略。
kubectl create clusterrolebinding permissive-binding \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--user=admin \
--user=kubelet \
--group=system:serviceaccounts