Table of Contents
[TOC]
Canal部署方案各角色如何协作
Canal中的角色
Canal中包含三种角色,分别是:
-
Canal server,通过canal-deployer部署,用于抽取binlog
-
Canal manager,canal的管理控制台,在canal server中被称为manager,代码在canal-admin子工程中,提供webui,可选
-
Zookeeper:用于存储元数据,canal instance的HA保障
相关源码简单阅读
canal server 与canal admin
打开canal的启动类CanalLauncher,在其main方法中可看到如下代码段:
com.alibaba.otter.canal.deployer.CanalLauncher
PlainCanal canalConfig = configClient.findServer(null);
executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
...
run
..
PlainCanal newCanalConfig = configClient.findServer(lastCanalConfig.getMd5());
这里是canal server通过canal admin获取server配置,有两处获取配置的代码:
-
启动时先获取server的配置配置,参数为null
-
默认每5秒获取一次配置,参数为上一次获取的配置的md5
获取配置后,有canalServer.start()方法的调用,用于启动canal server。
从CanalStarter.start()的调用中可以看到创建了CanalController,而CanalController的构造器中有如下代码片断:
instanceConfigMonitors = MigrateMap.makeComputingMap(new Function<InstanceMode, InstanceConfigMonitor>() {
public InstanceConfigMonitor apply(InstanceMode mode) {
int scanInterval = Integer.valueOf(getProperty(properties,
CanalConstants.CANAL_AUTO_SCAN_INTERVAL,
"5"));
if (mode.isSpring()) {
SpringInstanceConfigMonitor monitor = new SpringInstanceConfigMonitor();
monitor.setScanIntervalInSecond(scanInterval);
monitor.setDefaultAction(defaultAction);
// 设置conf目录,默认是user.dir + conf目录组成
String rootDir = getProperty(properties, CanalConstants.CANAL_CONF_DIR);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(rootDir)) {
rootDir = "../conf";
}
if (StringUtils.equals("otter-canal", System.getProperty("appName"))) {
monitor.setRootConf(rootDir);
} else {
// eclipse debug模式
monitor.setRootConf("src/main/resources/");
}
return monitor;
} else if (mode.isManager()) {
ManagerInstanceConfigMonitor monitor = new ManagerInstanceConfigMonitor();
monitor.setScanIntervalInSecond(scanInterval);
monitor.setDefaultAction(defaultAction);
String managerAddress = getProperty(properties, CanalConstants.CANAL_ADMIN_MANAGER);
monitor.setConfigClient(getManagerClient(managerAddress));
return monitor;
} else {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("unknow mode :" + mode + " for monitor");
}
}
});
在InstanceConfigMonitor中,会定时获取Instance配置。
打开canalServer.start()方法,在最后面有代码片断:
// start canalAdmin
String port = CanalController.getProperty(properties, CanalConstants.CANAL_ADMIN_PORT);
if (canalAdmin == null && StringUtils.isNotEmpty(port)) {
String user = CanalController.getProperty(properties, CanalConstants.CANAL_ADMIN_USER);
String passwd = CanalController.getProperty(properties, CanalConstants.CANAL_ADMIN_PASSWD);
CanalAdminController canalAdmin = new CanalAdminController(this);
canalAdmin.setUser(user);
canalAdmin.setPasswd(passwd);
String ip = CanalController.getProperty(properties, CanalConstants.CANAL_IP);
logger.debug("canal admin port:{}, canal admin user:{}, canal admin password: {}, canal ip:{}", port, user, passwd, ip);
CanalAdminWithNetty canalAdminWithNetty = CanalAdminWithNetty.instance();
canalAdminWithNetty.setCanalAdmin(canalAdmin);
canalAdminWithNetty.setPort(Integer.valueOf(port));
canalAdminWithNetty.setIp(ip);
canalAdminWithNetty.start();
this.canalAdmin = canalAdminWithNetty;
}
running = true;
此处有个canalAdminWithNetty.Start(),从类名和注解来看,这里用了netty并启动了canalAdmin,刚开始看到这里,我就有点懵逼了,这里有蹦出了个admin,manager所在的子工程也叫canal-admin,代码命名上不太友好,canal server中有与manager类似的概念,我们继续进入到canalAdminWithNetty.start()方法:
this.bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(new NioServerSocketChannelFactory(Executors.newCachedThreadPool(),
Executors.newCachedThreadPool()));
/*
* enable keep-alive mechanism, handle abnormal network connection
* scenarios on OS level. the threshold parameters are depended on OS.
* e.g. On Linux: net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 300
* net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 2 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl = 30
*/
bootstrap.setOption("child.keepAlive", true);
/*
* optional parameter.
*/
bootstrap.setOption("child.tcpNoDelay", true);
// 构造对应的pipeline
bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipelines = Channels.pipeline();
pipelines.addLast(FixedHeaderFrameDecoder.class.getName(), new FixedHeaderFrameDecoder());
// support to maintain child socket channel.
pipelines.addLast(HandshakeInitializationHandler.class.getName(),
new HandshakeInitializationHandler(childGroups));
pipelines.addLast(ClientAuthenticationHandler.class.getName(),
new ClientAuthenticationHandler(canalAdmin));
SessionHandler sessionHandler = new SessionHandler(canalAdmin);
pipelines.addLast(SessionHandler.class.getName(), sessionHandler);
return pipelines;
}
});
// 启动
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(ip)) {
this.serverChannel = bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(this.ip, this.port));
} else {
this.serverChannel = bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(this.port));
}
这里是使用了netty监听网络数据,端口则是canal.properties里配置的canal.admin.port,我们再来看看创建netty的Bootstrap所使用的ChannelPipeline,其中最重要的是SessionHandler,在SessionHandler中处理读取到的网络数据包:
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) throws Exception {
logger.info("message receives in session handler...");
ChannelBuffer buffer = (ChannelBuffer) e.getMessage();
Packet packet = Packet.parseFrom(buffer.readBytes(buffer.readableBytes()).array());
try {
String action = null;
String message = null;
String destination = null;
switch (packet.getType()) {
case SERVER:
ServerAdmin serverAdmin = ServerAdmin.parseFrom(packet.getBody());
action = serverAdmin.getAction();
switch (action) {
case "check":
message = canalAdmin.check() ? "1" : "0";
break;
case "start":
message = canalAdmin.start() ? "1" : "0";
break;
case "stop":
message = canalAdmin.stop() ? "1" : "0";
break;
case "restart":
message = canalAdmin.restart() ? "1" : "0";
break;
case "list":
message = canalAdmin.getRunningInstances();
break;
default:
byte[] errorBytes = AdminNettyUtils.errorPacket(301,
MessageFormatter.format("ServerAdmin action={} is unknown", action).getMessage());
AdminNettyUtils.write(ctx.getChannel(), errorBytes);
break;
}
AdminNettyUtils.write(ctx.getChannel(), AdminNettyUtils.ackPacket(message));
break;
case INSTANCE:
InstanceAdmin instanceAdmin = InstanceAdmin.parseFrom(packet.getBody());
destination = instanceAdmin.getDestination();
action = instanceAdmin.getAction();
switch (action) {
case "check":
message = canalAdmin.checkInstance(destination) ? "1" : "0";
break;
case "start":
message = canalAdmin.startInstance(destination) ? "1" : "0";
break;
case "stop":
message = canalAdmin.stopInstance(destination) ? "1" : "0";
break;
case "release":
message = canalAdmin.releaseInstance(destination) ? "1" : "0";
break;
case "restart":
message = canalAdmin.restartInstance(destination) ? "1" : "0";
break;
default:
byte[] errorBytes = AdminNettyUtils.errorPacket(301,
MessageFormatter.format("InstanceAdmin action={} is unknown", action).getMessage());
AdminNettyUtils.write(ctx.getChannel(), errorBytes);
break;
}
AdminNettyUtils.write(ctx.getChannel(), AdminNettyUtils.ackPacket(message));
break;
case LOG:
LogAdmin logAdmin = LogAdmin.parseFrom(packet.getBody());
action = logAdmin.getAction();
destination = logAdmin.getDestination();
String type = logAdmin.getType();
String file = logAdmin.getFile();
int count = logAdmin.getCount();
switch (type) {
case "server":
if ("list".equalsIgnoreCase(action)) {
message = canalAdmin.listCanalLog();
} else {
message = canalAdmin.canalLog(count);
}
break;
case "instance":
if ("list".equalsIgnoreCase(action)) {
message = canalAdmin.listInstanceLog(destination);
} else {
message = canalAdmin.instanceLog(destination, file, count);
}
break;
default:
byte[] errorBytes = AdminNettyUtils.errorPacket(301,
MessageFormatter.format("LogAdmin type={} is unknown", type).getMessage());
AdminNettyUtils.write(ctx.getChannel(), errorBytes);
break;
}
AdminNettyUtils.write(ctx.getChannel(), AdminNettyUtils.ackPacket(message));
break;
default:
byte[] errorBytes = AdminNettyUtils.errorPacket(300,
MessageFormatter.format("packet type={} is NOT supported!", packet.getType()).getMessage());
AdminNettyUtils.write(ctx.getChannel(), errorBytes);
break;
}
} catch (Throwable exception) {
byte[] errorBytes = AdminNettyUtils.errorPacket(400,
MessageFormatter.format("something goes wrong with channel:{}, exception={}",
ctx.getChannel(),
ExceptionUtils.getStackTrace(exception)).getMessage());
AdminNettyUtils.write(ctx.getChannel(), errorBytes);
}
}
看到这里也就明白了,这个CanalAdminWithNetty实际上就是给manager调用的,用于对canal做管理,在manager的webui上可以看到对应的功能:
那么canal server与canal manager之间是一个双向调用的关系:
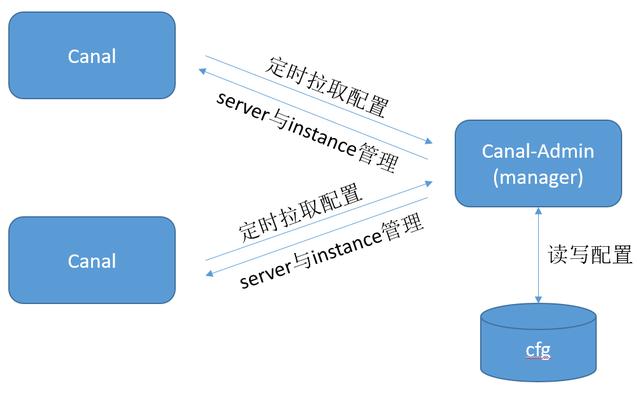
canal-admin有两个作用:
-
类似于配置中心,所有canal server从canal-admin定时摘取配置,包括server配置与instance配置,也就是canal.properties和instance.properties的内容
-
对canal server和canal instance的状态做管控,控制server/instance的启动停止等
canal server与canal-admin之间是双向调用,canal server即是canal-admin的客户端,同时也会响应canal admin的请求
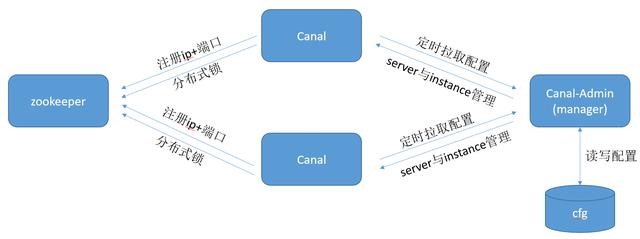
canal server与zookeeper
回到CanalController类,我们可以在start方法中看到,在启动时,会向zk注册一个临时节点,此目录包含当前机器的ip和端口(配置中的canal.registerIp, canal.port),当有新的session建议时,会重新注册该节点,很明显,这里类似于注册中心的作用,canal server启动时,先向zk注册自身的地址:
public void start() throws Throwable {
logger.info("## start the canal server[{}({}):{}]", ip, registerIp, port);
// 创建整个canal的工作节点
final String path = ZookeeperPathUtils.getCanalClusterNode(registerIp + ":" + port);
initCid(path);
if (zkclientx != null) {
// 向zk注册自身地址;
this.zkclientx.subscribeStateChanges(new IZkStateListener() {
public void handleStateChanged(KeeperState state) throws Exception {
}
public void handleNewSession() throws Exception {
initCid(path);
}
@Override
public void handleSessionEstablishmentError(Throwable error) throws Exception {
logger.error("failed to connect to zookeeper", error);
}
});
}
// 优先启动embeded服务
embededCanalServer.start();
// 尝试启动一下非lazy状态的通道
for (Map.Entry<String, InstanceConfig> entry : instanceConfigs.entrySet()) {
final String destination = entry.getKey();
InstanceConfig config = entry.getValue();
// 创建destination的工作节点
if (!embededCanalServer.isStart(destination)) {
// HA机制启动
ServerRunningMonitor runningMonitor = ServerRunningMonitors.getRunningMonitor(destination);
if (!config.getLazy() && !runningMonitor.isStart()) {
runningMonitor.start();
}
}
if (autoScan) {
instanceConfigMonitors.get(config.getMode()).register(destination, defaultAction);
}
}
if (autoScan) {
instanceConfigMonitors.get(globalInstanceConfig.getMode()).start();
for (InstanceConfigMonitor monitor : instanceConfigMonitors.values()) {
if (!monitor.isStart()) {
monitor.start();
}
}
}
// 启动网络接口
if (canalServer != null) {
canalServer.start();
}
}
在CanalController中,我们可以看到ServerRunningMonitor对象的创建代码:
final ServerRunningData serverData = new ServerRunningData(registerIp + ":" + port);
ServerRunningMonitors.setServerData(serverData);
ServerRunningMonitors.setRunningMonitors(MigrateMap.makeComputingMap(new Function<String, ServerRunningMonitor>() {
public ServerRunningMonitor apply(final String destination) {
ServerRunningMonitor runningMonitor = new ServerRunningMonitor(serverData);
runningMonitor.setDestination(destination);
runningMonitor.setListener(new ServerRunningListener() {
...
ServerRunningMonitor是针对每 一个destination的,即一个instance会创建一个ServerRunningMonitor,在ServerRunningMonitor.initRunning()方法中,会从zk上创建节点,成功则初始化instance,如果失败,则只从zk获取到运行instance的节点数据:
private void initRunning() {
if (!isStart()) {
return;
}
String path = ZookeeperPathUtils.getDestinationServerRunning(destination);
// 序列化
byte[] bytes = JsonUtils.marshalToByte(serverData);
try {
mutex.set(false);
zkClient.create(path, bytes, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL);
activeData = serverData;
processActiveEnter();// 触发一下事件
mutex.set(true);
release = false;
} catch (ZkNodeExistsException e) {
bytes = zkClient.readData(path, true);
if (bytes == null) {// 如果不存在节点,立即尝试一次
initRunning();
} else {
activeData = JsonUtils.unmarshalFromByte(bytes, ServerRunningData.class);
}
} catch (ZkNoNodeException e) {
zkClient.createPersistent(ZookeeperPathUtils.getDestinationPath(destination), true); // 尝试创建父节点
initRunning();
}
}
角色之间的关系总览
从CanalController与ServerRunningMonitor中可以看到有两处zk交互点,一个是注册自身的ip+端口,一个是创建节点并初始化instance(分布式锁),总体上看,三角色之间有如下交互关系:
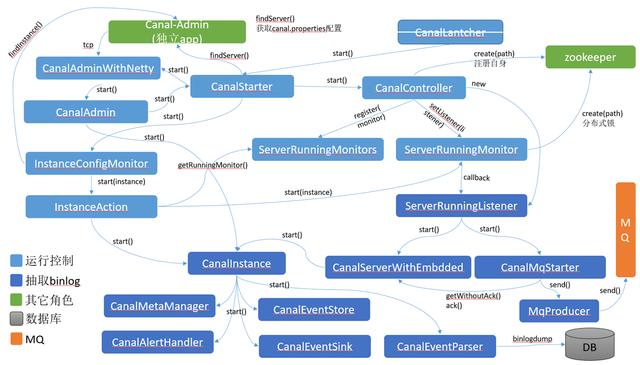
Canal的内部组件
Canal使用了组件生命周期管理的方式管理管理各个组件,有点类似于Tomcat,github上的原图:
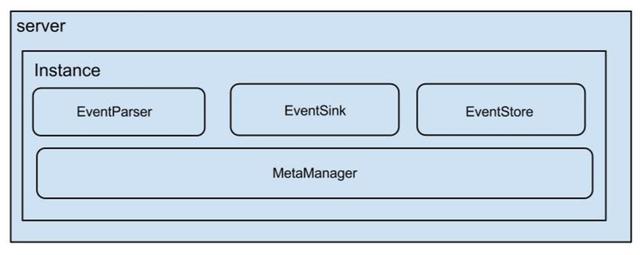
每一个组件都实现了CanalLifeCycle接口,该接口定义如下:
public interface CanalLifeCycle {
void start();
void stop();
boolean isStart();
}
内部组件之间的关系
Canal是一个多角色的分布式系统,除了binlog的抽取外,还有大量生命周期控制类的代码,以start()为例,主要组件之间的详细关系如下图: